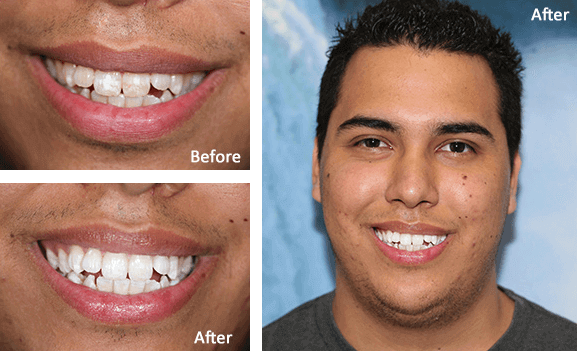
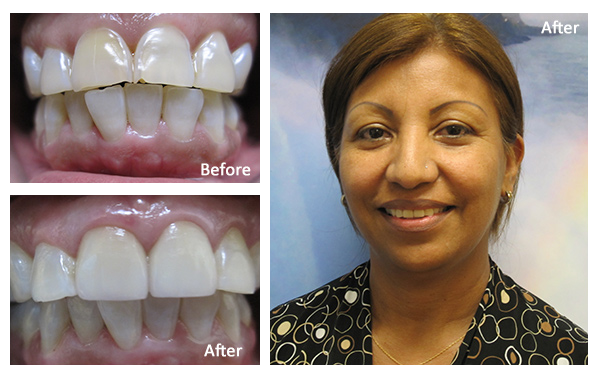
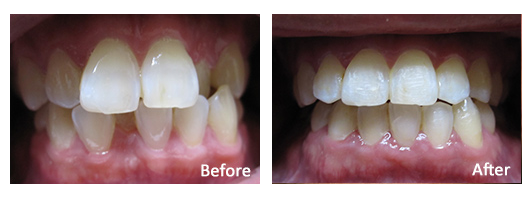
Smile Gallery
Dr. Luu and her team are proud to provide patients from the San Gabriel Valley with friendly, professional dental care. Browse our photo gallery and you will get to know us a little better!



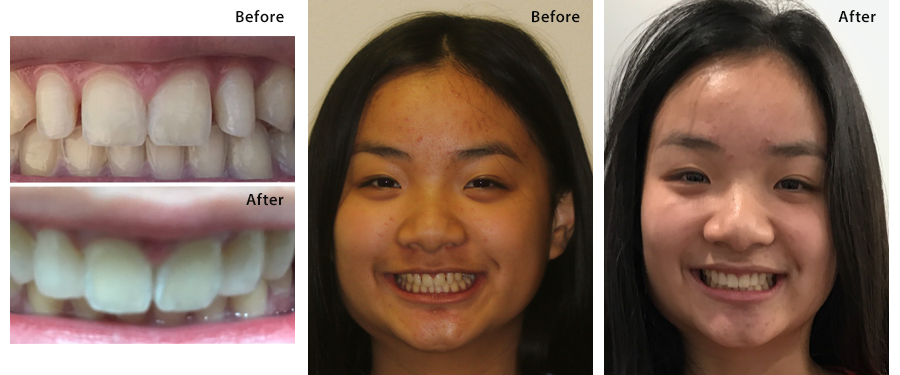

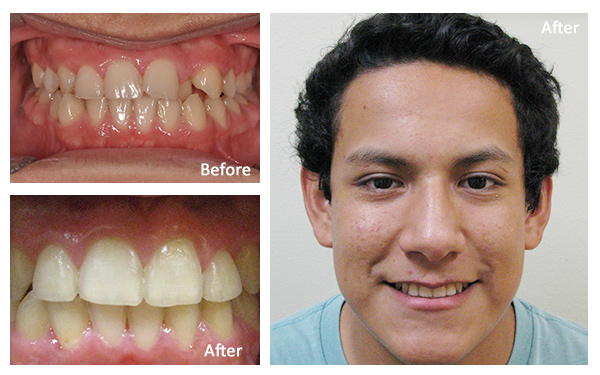
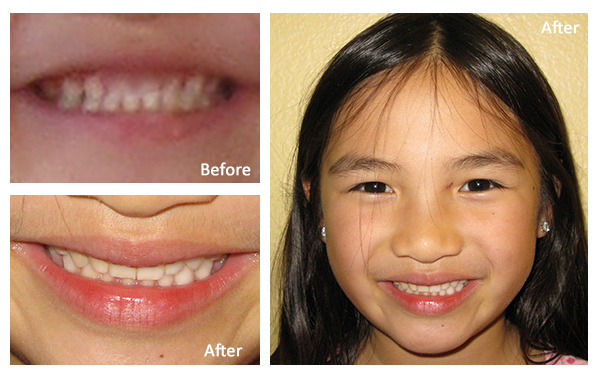
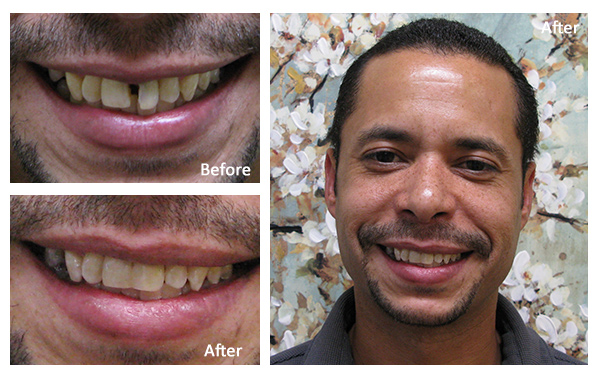












Dr. Brianne Luu speaks about Mercury Safe Fillings at Gentle Care Dentistry:
Hello my name is Doctor Luu and today I’m going to be talking about mercury safe dentistry. Now you might have heard that other offices say they don’t have mercury free dentistry. Mercury free is when you call an office and you need a filling and they don’t put any silver amalgam fillings they only do white. Our office is mercury safe because we follow certain protocols when we remove the silver fillings.
Now we do not place silver mercury fillings in your mouth. We do, do composite white porcelain bonding. When we do remove the silver fillings we follow certain protocols such as we use non latex rubber dam to isolate the teeth we are working on. We use a mask and oxygen tank to breathe so that you do not leave any of the mercury vapor that comes out when we take out your mercury silver fillings. In addition we have a wet towel over your face over your skin so if any remnants fall out it does not land on your skin. It lands on the paper towel. We also have a full body gown that we have you wear so that nothing lands on your skin or your clothes. In addition to all that we use a high speed low speed suction to take out the mercury remnants and also we use an evacuation system, high speed evacuation system that we place six inches from your mouth that collects the mercury vapor that comes out of your- when we take out the silver fillings and mercury fillings and it also collects any small remnants of the mercury silver fillings that may fall out.
So that’s the difference between our office which is mercury safe and mercury- other Mercury free offices. We want to protect you, we want to protect us, and we want to protect all our other patients.
Experienced dentist, wife and mother of three, Dr. Brianne Luu is committed to providing the most gentle, thorough and mercury-free dental care for patients of all ages.
Cosmetic Dentistry to Improve Your Smile:
Cosmetic Dentistry refer to a variety of dental procedures that may be used singly or in combination to make teeth and smiles more attractive. It’s focused mainly on the appearance of your teeth, mouth, and smile.
Do you have… Spaces or gaps between the teeth, discolored teeth, crooked teeth, gummy smiles, small or short teeth, crowded or rotated teeth, unsightly or stained fillings?
You can correct these issues ad more with the help of cosmetic dentistry.
Top 10 cosmetic dentistry procedures:
Teeth whitening, dental bonding, dental implants, dental veneers, dental crowns, dental bridges, dental fillings, cosmetic gum surgery, custom dentures, smile makeovers.
Why should you consider Cosmetic Dentistry? The benefits go far beyond cosmetic…
Enjoy better oral health with straighter easy to clean teeth
Improves self confidence
Improves the functionality and appearance of teeth
Most procedures offer instant results
Fight signs of aging with healthy and long lasting treatments
What’s New? Increased demand for natural-looking, tooth-coloured dental materials
Technological advancements; diagnostic lasers, intraoral cameras, tomography digital x-rays, and computer smile imaging.
Latest techniques such as smile lifts and dental facelifts, improved methods of payments and affordability.
Did you know?
A person’s smile outranked eyes, hair and body as the most important physical feature. Americans spends about $2.75 billion each year on cosmetic dentistry.
Two thirds of cosmetic dentistry patients are female and 33 percent are male.
Did you know?
50% of US citizens seek cosmetic dentistry to look good and feel younger, and 89% to improve physical attractiveness and self-esteem.
Did you know?
The most sought after treatment is Crown and bridges with a 97% turnaround.
It is never too late and you are never to old for Cosmetic Dentistry! Consult us to determine which cosmetic dental procedure is best for you.
Gentle Care Dentistry
Dr. Brianne Luu, DMD, MPH
Family & Cosmetic Dentistry
The 3 stages of gum disease are gingivitis, periodontitis, and advanced periodontitis. Gingivitis is caused by toxins irritating the gum line as a result of plaque build-up. Signs and symptoms of gingivitis includes swelling, sensitivity, and bleeding of the gums during brushing and flossing. Gingivitis can be easily reversed through professional care and good home oral hygiene. Periodontitis is categorized by irreversible bone loss that results from untreated gingivitis. The gums may begin to form a pocket below the gum line which traps food and plaque. Dental treatment and home care can help prevent from further damage, but at this stage, the results are not reversible. Advanced periodontitis is when the fibres and bones supporting the teeth destroyed. This may cause teeth to shift or loosen. Teeth may have to be removed depending on how advanced the disease has become and if treatments are not effective. You can begin by preventing gum disease with good oral health. Pick up a brochure or ask your dentist today.
A bridge is a non-surgical way to replace one or many teeth. A bridge uses the adjacent teeth as anchors to support the missing tooth or teeth. With today’s dental advancements, a bridge can be fabricated in a fairly short period of time, using a metal or non-metal foundation. Don’t let that missing tooth affect the way you speak, eat, and smile. Bridges yield immediate results that last a lifetime. Ask your dentist what type of bridge may be right for you.
Root canal therapy is a very common procedure. It has a reputation of being undesirable and painful but when done properly it is actually painless. Every tooth in your mouth is composed of a crown and a root. When a cavity or bacteria penetrates the tooth the root and its nerves become irritated. As a result the bacteria within the pulp cavity needs to be removed and cleaned in order to restore the tooth to its healthy state. Following the procedure the tooth is fragile and consequently is restored with a natural crown for a lifetime of durability. Root canals have a success rate of 95 percent or greater. Most root canals are diagnosed by patient’s sensitivities to a specific tooth. Be sure to consult your dentist if any symptoms or discomfort occur.
Dental Implants
Dental implants are titanium roots that are replaced within the jaw bones to resemble a tooth or a group of teeth. A screw is inserted through the gums and into the jaw bone. A porcelain crown is then attached to the screw to become the new tooth or teeth. They can be used to support dental prestices including crowns, dentures and bridges. Today’s treatments are so natural looking no one will know you had surgery. There is approximately a 95 percent success rate for all implants with modern advancements in dentistry some implants can be restored immediately with life like all porcelain crowns. For more details ask your dentist.
Veneers
Veneers are thin hand crafted porcelain shields worn on the front of the tooth which improves the appearance of teeth that are chipped, cracked, stained or worn. Veneers are as thin as contact lenses and are an aesthetically pleasing option of closing gaps, lengthening teeth and providing symmetry to make your smile more natural. Veneers are intended to last for many years without changing colour. They are one of the most popular cosmetic procedures in dentistry. Ask your dentist if veneers maybe right for you.
Fact or myth? If you have a cavity, you will know it. Myth, mild tooth decay has no symptoms. Sensitivity begins to occur when the tooth decay is already causing damage to the nerve. Today’s dentistry prevents tooth decay with sealants and other conservative methods. Fact or myth? Sugar is the prime cause of cavities. A fact and also a myth. Acid is the main trigger in producing the bacteria that causes cavities. The bacteria is then fueled by the consumption of carbohydrates. Sugar is a trigger in cavities, but carbs as a whole are the main cause. Fact or myth? Cavities are the prime reason for root canals. Myth. Root canals are a result of nerve damage. And untreated cavity could lead to nerve damage, but root canals are on set by number of different factors. Facts on myth? Brushing and flossing are the best way to prevent cavities. Fact.
Fact or myth? Expensive toothpastes are always better than cheaper ones. Myth. Different toothpastes are better for different teeth in situations. Sometimes moderately priced toothpaste can be more effective. Ask the dentist about what might be best for your teeth. And always look for the ADA seal of approval. Fact or myth? If a tooth is white, it must be healthy. Myth. Under the surface there may be cavities, problems with the root or other abnormalities. Fact or Myth? Teeth whitening is harmful because it damages enamel. Myth. There are many modern teeth whitening processes that have minimal harmful effects. Teeth whitening isn’t for every mouth or person though. Consult the dentist before you proceed with whitening treatments. Fact or myth? Dentists should be feared. Myth. With today’s advancements in technology and safety practices there is nothing to worry about. Procedures are as quick and painless as ever. Fact or myth? You should visit your dentists at least twice a year. FACT.
Mercury is one of the most toxic elements and a persistent traveller for our environment. So who’s the travel agent for this elemental poison? Coal-fired power plants most definitely. Mining operations, of course. Your neighbourhood dental office? Surprisingly yes! The United Nations Environment Program propose that 10% of global mercury usage is for amalgam tooth fillings. This results in up to 340 tons of dental mercury journeying into the environment each year. In the United States dentists are currently the second largest users of elemental mercury. This accounts for roughly 32 tons of mercury used yearly to place amalgam restorations otherwise known as silver fillings. Although the number of amalgam’s placed has decreased over the last few decades dentists still use amalgam without precautions. So the threat of mercury exposure continues. Dental mercury travels many pathways on its journey back into the environment. It starts when a dentist receives pre capsulated dental amalgam. Each capsule up to 900 milligrams of elemental mercury is separated from the other alloys. To make the final product the capsule is vigorously shaken in a traitor. The thoroughly mix all the elements. Occupational safety concerns arise because this heats the mercury creating thousands of micrograms of mercury vapour which are released upon opening the capsule. The used amalgam capsule still contains a small amount of mercury. So the ADA recommends the capsules be stored in an airtight container and collected by a hazardous waste company. Unfortunately the majority of dentists tossed the capsules into the trash. This mercury contaminated trash will eventually travel to a landfill where the mercury will continue its trek down into the soil. Back at the dental office the freshly mixed amalgam is placed into the tooth. The dentist then carves away any excess material. While patients swallow some amalgam waste most is suction down and flows through a filtration system, but this system only captures a small percent of the larger pieces. The vast majority at much smaller pieces escape into waste water. A similar scenario plays out when dentists replace amalgam fillings. Many dentists not realizing the environmental harm clean out their filtration systems by dumping the captured mercury tainted sludge down the drain. A study funded by the ADA estimated that amalgam fillings contribute up to 50% of the mercury found in wastewater. This contaminated water then flows two publicly owned water treatment plants. While efforts are made to mercury from wastewater most of it settles down into the sewage sludge which is then taken and spread on land as fertilizer or deposited in a landfill. In both scenarios the mercury constantly off gases into the atmosphere and seeps into the ground. The percentage of the sewage sludge is also sent packing to incinerators. With over 200 tons of dental mercury continually off gassing mercury vapour in the mouths of Americans even exhaling is a contributor of mercury to our atmosphere. Additionally people with amalgam fillings serve as hosts for Mercury’s passage back into our environment through the excretion of human waste. Mercury’s ride continues even after death. Crematories which are unregulated and contain no filtering processes are growing vehicle for transporting mercury back into the atmosphere. When all the various pathways are accounted for dental mercury from the United States contributes roughly twenty eight and a half tons into the environment each year. The governments of the world are actively working together to reduce the amount of mercury released globally to protect human health. The first and most powerful step to eliminating mercury release from dental amalgam is to discontinue the use of this toxic material. With the threat so great and the solution is so simple it’s time to restrict Mercury’s Passport.
Teeth whitening
At a young age, our teeth are healthy and white but over time the enamel coating the tooth is slowly worn down causing our teeth to become stained and yellow which is why teeth whitening is becoming increasingly popular today. There are a few methods for whitening – they include at home and in office. With in-office treatments you will see faster results, receive the safest treatments for bleaching the teeth and yield the whitest smile. So don’t settle for teeth that have become stained from years of coffee drinking, tobacco use or just ageing. Ask your dentist about whitening options that maybe right for you.
The maintenance of clean teeth and gums revolves around brushing and flossing. Place the toothbrush bristles next to the gum line on the outer surfaces of the teeth. Brush gently using a back-and-forth technique with the toothbrush. For the inner surface of the teeth place the bristles next to the gum line and brush in a circular motion. The inside of the mouth is where the most plaque accumulates. Brush the surface of the teeth where the chewing of food takes place in the same circular motion. To clean those places between the teeth wear a toothbrush can’t reach floss once a day to remove food and plaque before it can cause gum disease. So eat a well-balanced diet, brush twice daily, and schedule regular check-ups with the dentist.











